-
What is this?
Kain & Fowler's prescient review from October 2019 sets out how intensive care units should prepare and respond to the next pandemic, both practically at a hospital level and at a wider health-system. Although the focus was on an influenza pandemic, the advice is readily applicable to the SARS-COV-2 pandemic.
Background
They note that not only have we seen regular influenza outbreaks in addition to other viral pandemics, that due to increased urbanisation, population density, global travel and living proximity to animals, there is rapidly increasing global risk of a viral pandemic.
"When considering preparation for the next pandemic, it is not a matter of if it will occur, but rather a matter of when." – Kain & Fowler
They provide an overview of historical influenza pandemics over the last century, most recently with the 2009 H1N1 swine-flu pandemic, killing 300,000 people.
- Despite this history we remain unprepared for a pandemic.
- From an ICU perspective, conservative models predict >170% ICU resource utilisation due to a pandemic. They note that most health systems would struggle with even this optimistic surge.
- SARS experience in Canada, despite only 251 cases, critically stretched hospital and ICU resources.
What preparation do they recommend?
Kain and Fowler suggest global focus on:
- Pandemic surveillance.
- Prepare health-system scalability to manage surge: equipment, physical space, human resources, and system (eg. stepped triage plans).
- Prepare for mass vaccine production.
- Better coordinate and integrate communications.
- Streamlined research and ethics proposals for rapid initiation.
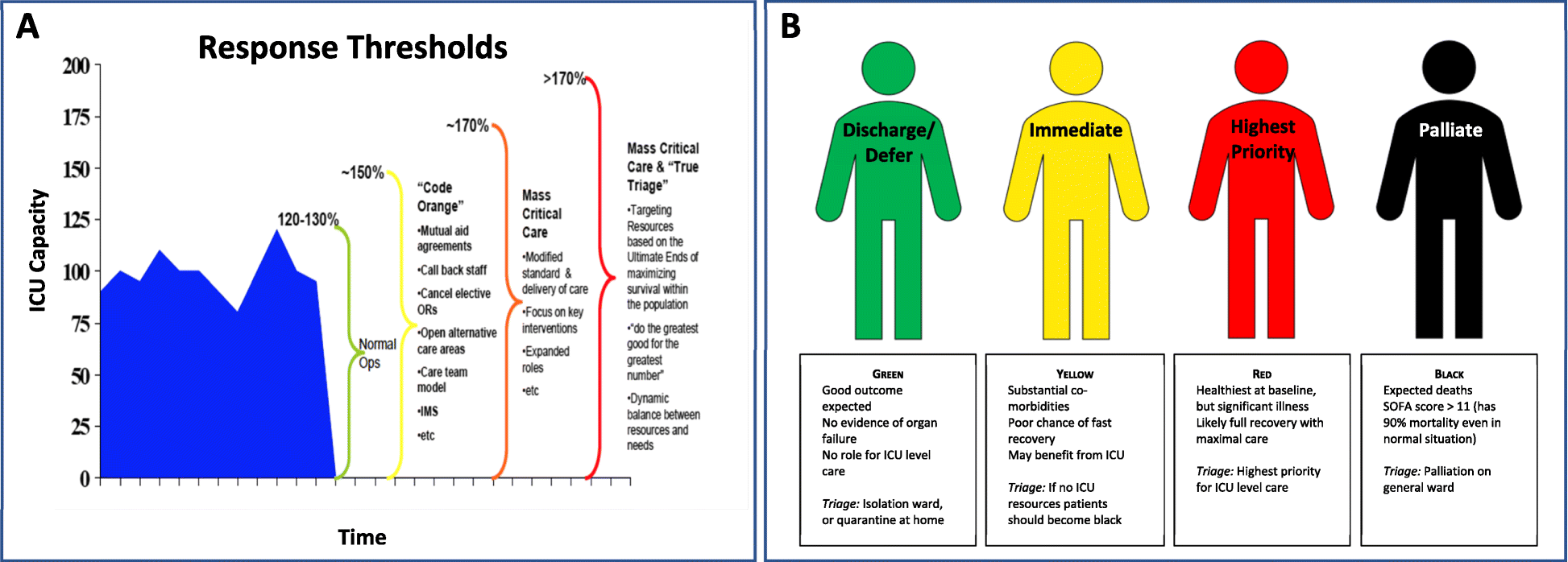
They highlight the importance of intensivists being involved in strategic planning, so as to coordinate ICU responses for "...triage, clinical care, and infection control." – noting that during SARS 20% of infections were in healthcare workers, and hospitals themselves became important sources of transmission.
Final word...
The IHR Committee's review following the 2009 H1N1 pandemic is now only too obvious:
summary“...the world is ill-prepared to respond to a severe influenza pandemic or to any similarly global, sustained, and threatening public-health emergency.” – International Health Regulations Committee (2011)
- Taylor Kain and Robert Fowler.
- Department of Critical Care, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada.
- Crit Care. 2019 Oct 30; 23 (1): 337337.
AbstractFew viruses have shaped the course of human history more than influenza viruses. A century since the 1918-1919 Spanish influenza pandemic-the largest and deadliest influenza pandemic in recorded history-we have learned much about pandemic influenza and the origins of antigenic drift among influenza A viruses. Despite this knowledge, we remain largely underprepared for when the next major pandemic occurs.While emergency departments are likely to care for the first cases of pandemic influenza, intensive care units (ICUs) will certainly see the sickest and will likely have the most complex issues regarding resource allocation. Intensivists must therefore be prepared for the next pandemic influenza virus. Preparation requires multiple steps, including careful surveillance for new pandemics, a scalable response system to respond to surge capacity, vaccine production mechanisms, coordinated communication strategies, and stream-lined research plans for timely initiation during a pandemic. Conservative models of a large-scale influenza pandemic predict more than 170% utilization of ICU-level resources. When faced with pandemic influenza, ICUs must have a strategy for resource allocation as strain increases on the system.There are several current threats, including avian influenza A(H5N1) and A(H7N9) viruses. As humans continue to live in closer proximity to each other, travel more extensively, and interact with greater numbers of birds and livestock, the risk of emergence of the next pandemic influenza virus mounts. Now is the time to prepare and coordinate local, national, and global efforts.
Notes
What is this?
Kain & Fowler's prescient review from October 2019 sets out how intensive care units should prepare and respond to the next pandemic, both practically at a hospital level and at a wider health-system. Although the focus was on an influenza pandemic, the advice is readily applicable to the SARS-COV-2 pandemic.
Background
They note that not only have we seen regular influenza outbreaks in addition to other viral pandemics, that due to increased urbanisation, population density, global travel and living proximity to animals, there is rapidly increasing global risk of a viral pandemic.
"When considering preparation for the next pandemic, it is not a matter of if it will occur, but rather a matter of when." – Kain & Fowler
They provide an overview of historical influenza pandemics over the last century, most recently with the 2009 H1N1 swine-flu pandemic, killing 300,000 people.
- Despite this history we remain unprepared for a pandemic.
- From an ICU perspective, conservative models predict >170% ICU resource utilisation due to a pandemic. They note that most health systems would struggle with even this optimistic surge.
- SARS experience in Canada, despite only 251 cases, critically stretched hospital and ICU resources.
What preparation do they recommend?
Kain and Fowler suggest global focus on:
- Pandemic surveillance.
- Prepare health-system scalability to manage surge: equipment, physical space, human resources, and system (eg. stepped triage plans).
- Prepare for mass vaccine production.
- Better coordinate and integrate communications.
- Streamlined research and ethics proposals for rapid initiation.

They highlight the importance of intensivists being involved in strategic planning, so as to coordinate ICU responses for "...triage, clinical care, and infection control." – noting that during SARS 20% of infections were in healthcare workers, and hospitals themselves became important sources of transmission.
Final word...
The IHR Committee's review following the 2009 H1N1 pandemic is now only too obvious:
“...the world is ill-prepared to respond to a severe influenza pandemic or to any similarly global, sustained, and threatening public-health emergency.” – International Health Regulations Committee (2011)
Knowledge, pearl, summary or comment to share?You can also include formatting, links, images and footnotes in your notes
- Simple formatting can be added to notes, such as
*italics*,_underline_or**bold**. - Superscript can be denoted by
<sup>text</sup>and subscript<sub>text</sub>. - Numbered or bulleted lists can be created using either numbered lines
1. 2. 3., hyphens-or asterisks*. - Links can be included with:
[my link to pubmed](http://pubmed.com) - Images can be included with:
 - For footnotes use
[^1](This is a footnote.)inline. - Or use an inline reference
[^1]to refer to a longer footnote elseweher in the document[^1]: This is a long footnote..